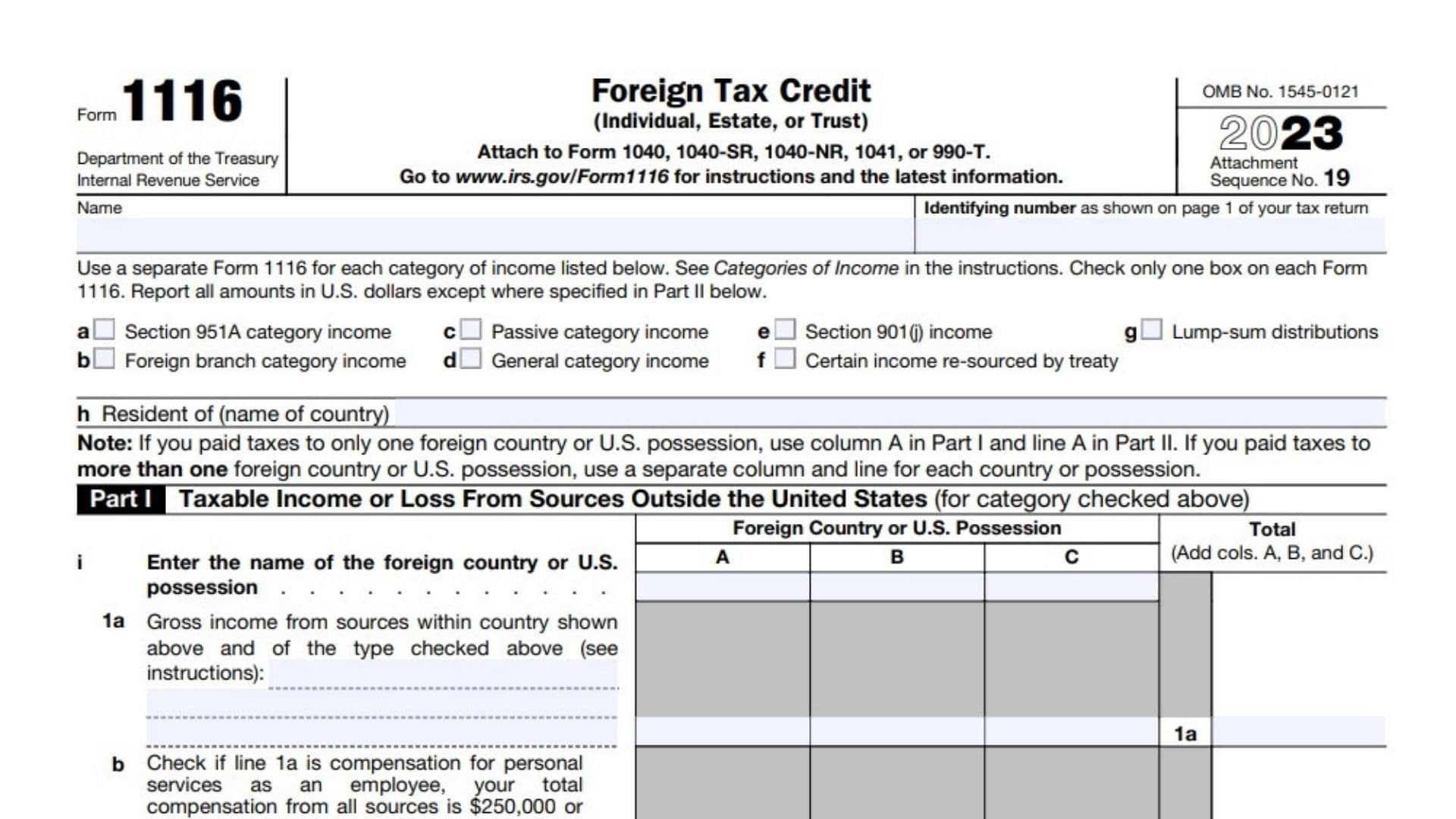
Form 1116, the Foreign Tax Credit form, is an essential document for U.S. taxpayers with income from foreign sources. Understanding and correctly filing this form can help you avoid double taxation and maximize your tax benefits. The primary purpose of Form 1116 is to help U.S. taxpayers claim a credit for taxes paid to foreign governments. This credit is crucial as it prevents double taxation on income that has already been taxed by another country. The United States taxes its citizens and residents on their worldwide income, but Form 1116 provides a way to offset the taxes paid to foreign jurisdictions, thereby reducing the overall tax burden. This form essentially allows you to subtract the amount of foreign taxes paid from your U.S. tax liability, which can lead to significant tax savings. By doing so, it helps promote international trade and investment by minimizing the tax disadvantages that can arise from cross-border transactions.
Who Must File Form 1116?
Any U.S. taxpayer who has paid or accrued foreign taxes on foreign income should consider filing this form. This includes U.S. citizens, resident aliens, and some nonresident aliens who have foreign income that is also subject to U.S. taxation. If you have received dividends, interest, rents, royalties, or wages from foreign sources, or if you own shares in a foreign corporation, you may need to file Form 1116. Additionally, if you are a partner in a partnership, a shareholder in an S corporation, or a beneficiary of an estate or trust that has foreign income, you will also need to file. However, if your total foreign taxes paid do not exceed $300 ($600 for married filing jointly), you might be able to claim the Foreign Tax Credit directly on your Form 1040 without filing Form 1116.
How to File Form 1116?
Filing Form 1116 involves several steps and can be done electronically or by mail, along with your annual tax return. First, you need to determine if you qualify for the Foreign Tax Credit. Then, gather all necessary documentation, including records of foreign taxes paid and details about your foreign income. The form can be downloaded from the IRS website. When completing the form, you need to enter information about your foreign income and taxes paid, as well as calculate the credit limit based on the Internal Revenue Code. It’s important to note that accurate record-keeping and documentation are crucial for this process, as the IRS may request proof of the foreign taxes paid. After filling out the form, attach it to your federal tax return (Form 1040, 1040-SR, or 1040-NR). If you are filing electronically, tax software can guide you through the process. Ensure you meet all filing deadlines to avoid penalties and interest.

How to Complete Form 1116?
Filling out Form 1116 requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of your foreign income and taxes. Form 1116 is divided into several parts, each addressing different aspects of your foreign tax situation.
- Part I – Taxable Income or Loss from Sources Outside the United States: Here, you report your foreign income and the type of income it is (e.g., passive income, general category income).
- Part II – Foreign Taxes Paid or Accrued: This section requires you to list the foreign taxes you paid or accrued during the tax year. You need to provide information such as the name of the foreign country and the type of tax paid.
- Part III – Figuring the Credit: This part involves calculating the credit limit, which can be complex. It requires you to determine the amount of foreign taxes that are eligible for the credit and compare it to your U.S. tax liability on the same income.
- Part IV – Summary of Credits From Separate Parts III: If you have income from multiple foreign sources, you may need to fill out more than one Form 1116. Part IV is where you summarize the credits from these multiple forms.