Form 8938 is an IRS form that U.S. taxpayers use to report specified foreign financial assets if their total value exceeds a certain threshold. This form is part of the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) and is designed to ensure compliance with U.S. tax laws regarding foreign financial assets. The form requires taxpayers to provide detailed information on their foreign financial accounts, including deposit accounts, custodial accounts, and other foreign assets like stocks, bonds, and ownership in foreign entities. The form is divided into several parts, including sections for reporting the maximum value of foreign accounts, income generated from these assets, and whether the assets were acquired or disposed of during the tax year. Filing Form 8938 is mandatory if you meet the reporting threshold, and failing to do so can result in significant penalties. Form 8938 must be attached to your annual tax return (Form 1040, 1120, etc.) and submitted to the IRS.

How to Complete Form 8938?
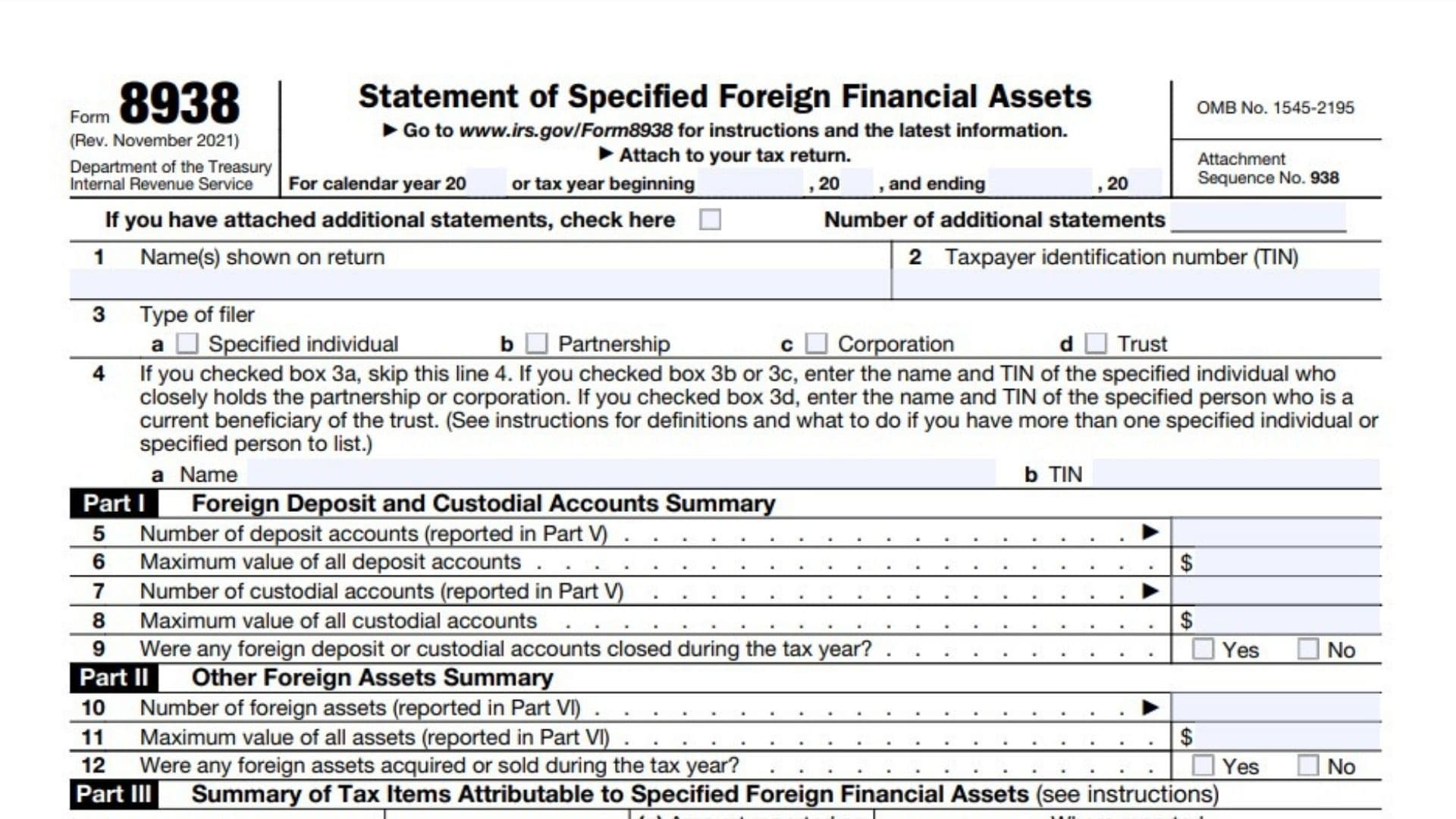
Part I – Foreign Deposit and Custodial Accounts Summary
- Line 5 – Number of Deposit Accounts
Enter the number of foreign deposit accounts you hold. This includes bank accounts, savings accounts, and other types of deposit accounts. - Line 6 – Maximum Value of All Deposit Accounts
Report the highest aggregate value of all your foreign deposit accounts during the tax year. Convert the foreign currency into U.S. dollars using the correct exchange rate. - Line 7 – Number of Custodial Accounts
Enter the number of foreign custodial accounts (such as brokerage accounts) you hold. - Line 8 – Maximum Value of All Custodial Accounts
Report the highest value of your custodial accounts during the tax year, converted into U.S. dollars. - Line 9 – Closed Accounts
Indicate whether any of your foreign deposit or custodial accounts were closed during the tax year by checking either “Yes” or “No.”
Part II – Other Foreign Assets Summary
- Line 10 – Number of Foreign Assets
Enter the total number of foreign financial assets you hold that are not deposit or custodial accounts, such as foreign stocks, bonds, or ownership interests in foreign companies. - Line 11 – Maximum Value of All Assets
Report the highest aggregate value of all other foreign financial assets during the tax year, converted into U.S. dollars. - Line 12 – Acquired or Sold Assets
Indicate whether any foreign financial assets were acquired or sold during the tax year by checking “Yes” or “No.”
Part III – Summary of Tax Items Attributable to Specified Foreign Financial Assets
- Line 13 – Foreign Deposit and Custodial Accounts
Report the tax items (e.g., interest, dividends, gains, and losses) attributable to your foreign deposit and custodial accounts. Use the following categories:
- Interest
- Dividends
- Royalties
- Other income
- Gains (losses)
- Deductions
- Credits
- Line 14 – Other Foreign Assets
Report the tax items attributable to your other foreign financial assets, using the same categories as in Line 13.
Part IV – Excepted Specified Foreign Financial Assets
- Lines 15-19 – Forms Filed
If you have already reported any of your specified foreign financial assets on other IRS forms, such as Form 3520, Form 5471, or Form 8621, list them here. You do not need to report the same assets again on Form 8938.
Part V – Detailed Information for Each Foreign Deposit and Custodial Account
- Line 20 – Type of Account
Check whether the account is a deposit account or a custodial account. - Line 21 – Account Number
Enter the account number or other designation that identifies the account. - Line 22 – Account Status
Check the appropriate boxes if the account was opened or closed during the tax year or if it is jointly owned with a spouse. - Line 23 – Maximum Value of Account
Report the maximum value of the account during the tax year in U.S. dollars. - Line 24 – Foreign Currency Exchange Rate
Indicate whether you used a foreign currency exchange rate to convert the account value into U.S. dollars. If “Yes,” proceed to Line 25. - Lines 25-28 – Foreign Currency Details
Provide details about the foreign currency in which the account is maintained, the exchange rate used, and the source of the exchange rate (if not from the U.S. Treasury Department). - Line 26 – Financial Institution Information
Enter the name, address, and Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) of the financial institution where the account is held.
Part VI – Detailed Information for Each Other Foreign Asset
- Line 29 – Description of Asset
Describe the foreign financial asset, such as foreign stocks, bonds, or ownership interests in a foreign entity. - Line 30 – Identifying Number
Provide the identifying number or other designation related to the asset. - Lines 31-32 – Asset Status and Value
Report the date the asset was acquired or disposed of and the maximum value of the asset during the tax year. - Line 33 – Foreign Currency Conversion
Indicate whether a foreign currency exchange rate was used to convert the asset value into U.S. dollars. - Lines 34-36 – Additional Details for Foreign Assets
If applicable, provide additional details about the foreign entity or issuer related to the foreign asset, including the name, type (e.g., corporation, partnership), and address of the entity.
Notes
- Form 8938 is required if your total foreign financial assets exceed the IRS reporting thresholds.
- You must report detailed information on foreign deposit accounts, custodial accounts, and other foreign financial assets.
- Filing the form accurately is essential to avoid penalties; consult with a tax professional if needed.