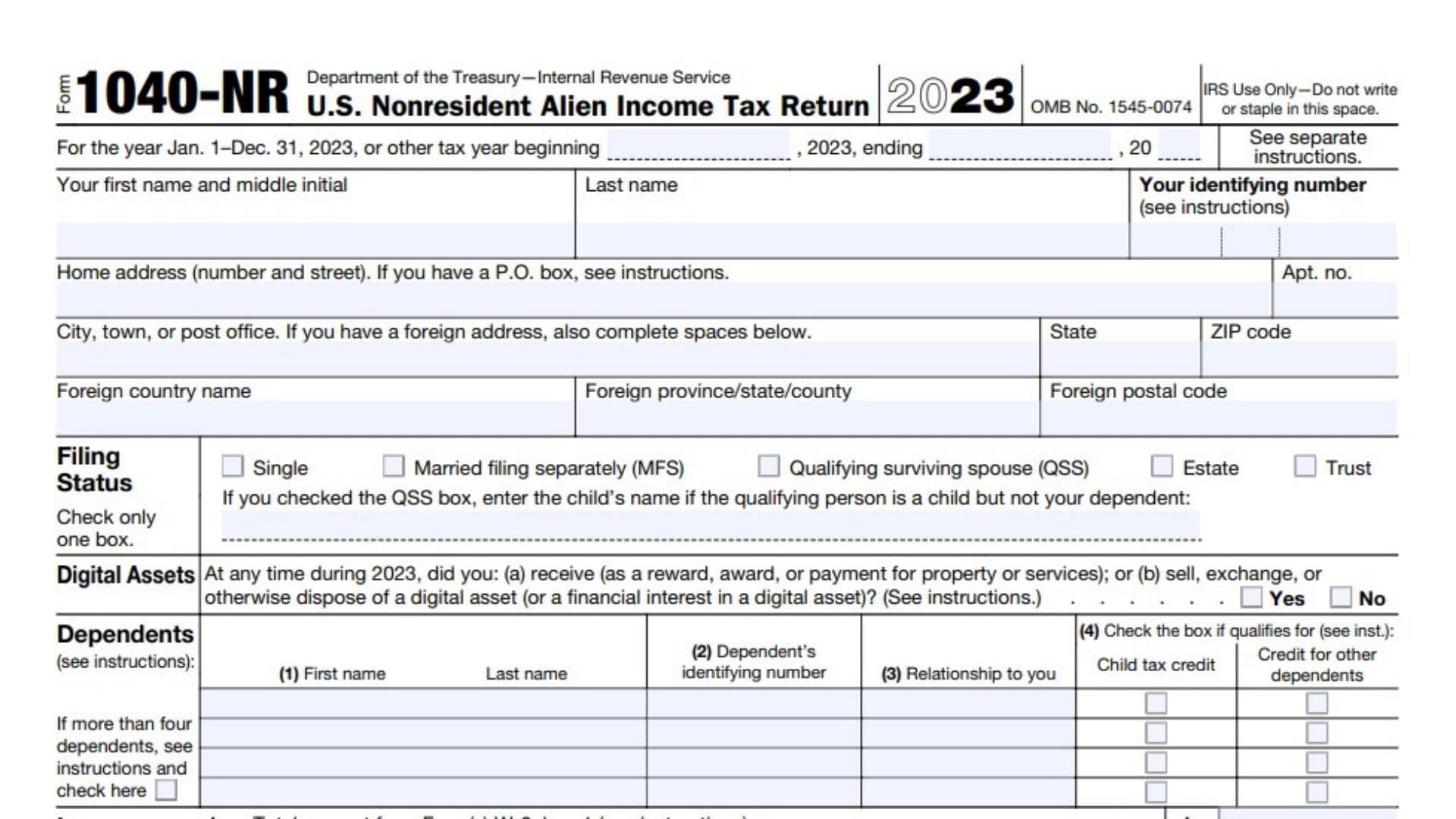
Form 1040-NR, known as the U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return, is used by nonresident aliens who have U.S. source income. This form allows nonresident aliens to report their income and claim deductions and credits, ensuring they pay the correct amount of U.S. taxes. The form includes sections for various types of income, deductions, and credits that apply specifically to nonresident aliens.
Nonresident aliens must file Form 1040-NR if they have any of the following types of income:
- U.S. Source Income: Wages, salaries, tips, and other compensation for services performed in the U.S.
- Investment Income: Interest, dividends, rents, and royalties from U.S. sources.
- Business Income: Income from a business or trade operated in the U.S.
- Other Income: Certain types of income such as scholarship or fellowship grants.
Additionally, nonresident aliens who are engaged in a trade or business in the U.S., regardless of whether they have income from that business, must file Form 1040-NR.
How to File Form 1040-NR?
Filing the IRS Form 1040-NR involves several steps:
- Obtain the Form: Nonresident aliens can obtain Form 1040-NR from the IRS website or through tax preparation software.
- Complete the Form: Fill out the form with the required information about income, deductions, credits, and tax liability.
- Submit to the IRS: File the form by mailing it to the appropriate IRS address. Currently, electronic filing is not available for Form 1040-NR.
- Include Attachments: Attach any required forms and schedules that provide additional information about your income and deductions.

How to Complete Form 1040-NR?
Completing the Form 1040-NR requires detailed information about the nonresident alien’s U.S. income and deductions. Here’s how to do it:
- Personal Information: Enter your name, address, taxpayer identification number (TIN), and country of citizenship.
- Filing Status: Indicate your filing status, such as single nonresident alien or married nonresident alien.
- Income Section: Report all sources of U.S. income, including wages, salaries, tips, interest, dividends, rents, royalties, and business income.
- Adjustments to Income: Calculate and enter any adjustments to income, such as contributions to an IRA or student loan interest deductions.
- Deductions and Credits: Claim any allowable deductions and credits to reduce your taxable income and tax liability.
- Tax Calculation: Calculate your total tax liability using the tax tables or tax computation worksheets provided by the IRS.
- Payments and Refundable Credits: Enter any tax payments made during the year, including federal income tax withheld and estimated tax payments.
- Refund or Amount You Owe: Calculate whether you are due a refund or if you owe additional taxes. Provide your bank account information for direct deposit if you are owed a refund.
- Signature: Sign and date the form. If you have a representative preparing your return, they must also sign and provide their information.
Review all entries for accuracy and completeness before submitting the form.
Additional Considerations for Nonresident Aliens
- Treaty Benefits: Nonresident aliens from countries with tax treaties with the U.S. may be eligible for reduced tax rates or exemptions. Attach Form 8833, Treaty-Based Return Position Disclosure, if you are claiming treaty benefits.
- Dual-Status Aliens: If you were a resident alien for part of the year and a nonresident alien for the rest, you may need to file both Form 1040 and Form 1040-NR. Consult IRS Publication 519, U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens, for guidance.
- Social Security and Medicare Taxes: Nonresident aliens working in the U.S. under certain visa types (e.g., F-1, J-1, M-1, Q-1) may be exempt from Social Security and Medicare taxes. Employers should be informed of this exemption.
Where to Mail Form 1040-NR?
The mailing address for Form 1040-NR depends on whether the nonresident alien is including a payment with the form. The IRS provides specific addresses for different situations, which are listed in the form’s instructions. It is important to use the correct address to ensure timely processing.

Due Dates
The Form 1040-NR must be filed by the 15th day of the 4th month after the end of the tax year, which is typically April 15th. However, nonresident aliens who are not employees subject to U.S. income tax withholding have until June 15th to file. If you cannot file by the due date, you can request an extension by filing Form 4868, which grants an additional six months to file the return. However, any taxes owed must still be paid by the original due date to avoid interest and penalties.
Variants of Form 1040-NR
There are related forms and schedules that nonresident aliens may need to file along with Form 1040-NR:
- Schedule NEC (Form 1040-NR): Used to report income not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business.
- Schedule OI (Form 1040-NR): Provides other information, such as details about visa status and days of presence in the U.S.
- Form 8843: Statement for Exempt Individuals and Individuals With a Medical Condition – Used to claim exemption from the substantial presence test.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I file Form 1040-NR electronically?Currently, Form 1040-NR must be filed by mail. The IRS does not offer an electronic filing option for this form.
- Do I need an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) to file Form 1040-NR?Yes, nonresident aliens who do not have a Social Security number must obtain an ITIN to file Form 1040-NR.
- What happens if I fail to file Form 1040-NR?Failure to file Form 1040-NR can result in penalties, interest on any unpaid taxes, and potential legal consequences. It is important to file on time and comply with IRS requirements.