IRS Form W-12 is the official form used to apply for or renew a Paid Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN). A PTIN is a unique number issued by the IRS to tax return preparers who prepare or assist in preparing federal tax returns for compensation. This number is required for tax professionals to legally prepare tax returns. The form collects identifying information, professional credentials, compliance status, and includes payment for the application processing fee. Whether you are applying for the first time or renewing your PTIN for upcoming tax years, Form W-12 is the necessary step to maintain legal authorization to prepare federal returns.
How To File IRS Form W-12
You can file Form W-12 either online or by mail. The online method provides an immediate issuance of your PTIN after completing the form on the IRS website at www.irs.gov/ptin. If mailing, complete the paper form and send it to:
IRS Tax Professional PTIN Processing Center
PO Box 380638
San Antonio, TX 78268
Allow about 6 weeks for mailed applications to process. Incomplete applications or failure to supply requested information will delay processing or cause rejection.

How To Complete Form W-12
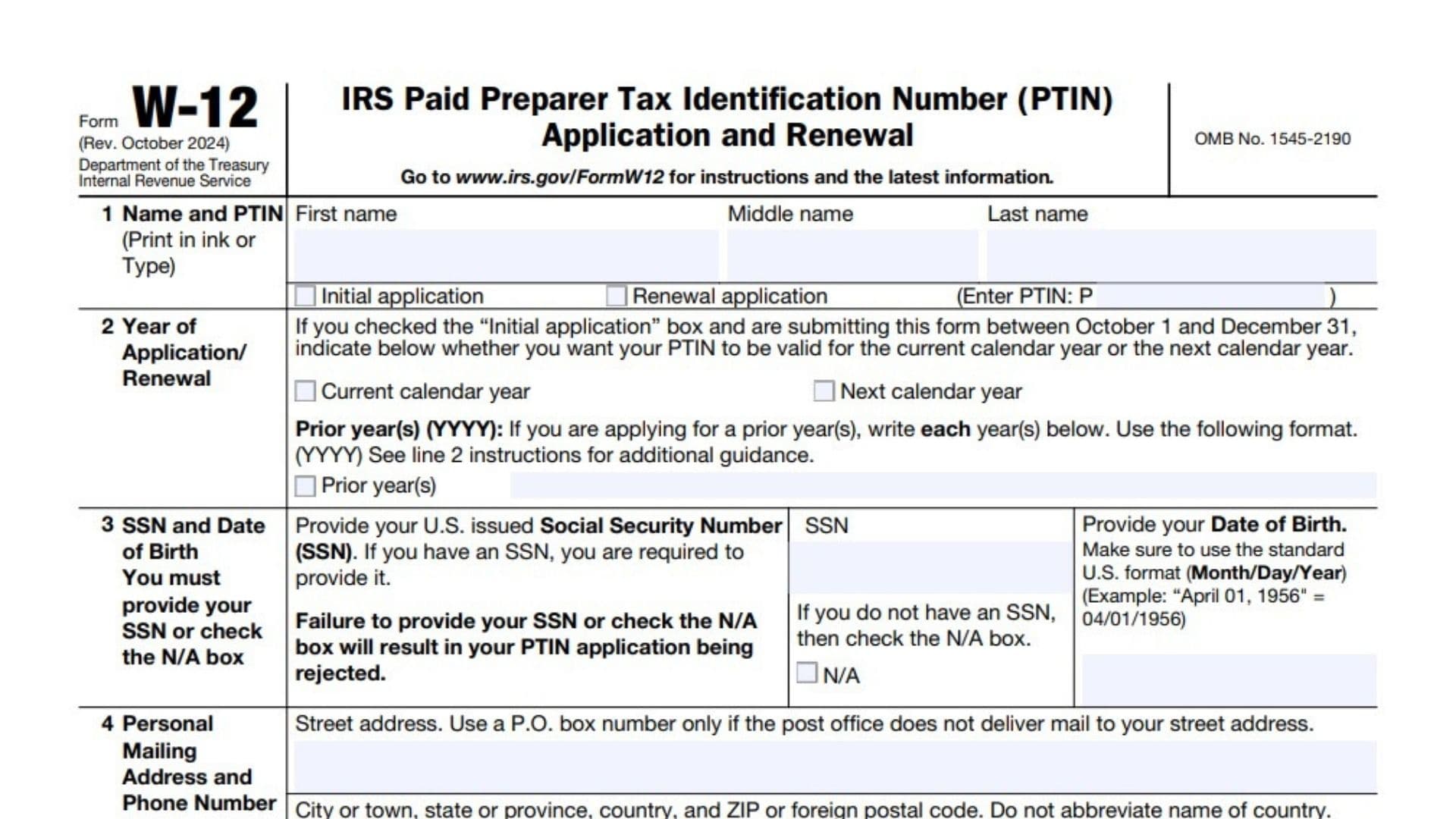
Line 1: Name and PTIN
Print your first, middle, and last names clearly. For an initial application, check “Initial application.” For renewal, check “Renewal application” and enter your current PTIN number starting with “P.”
Line 2: Year of Application/Renewal
If applying between October 1 and December 31 and this is an initial application, indicate whether your PTIN should be valid for the current calendar year or the next calendar year. You may also apply for prior years by listing the years in the YYYY format.
Line 3: Social Security Number (SSN) and Date of Birth
You must enter your U.S.-issued Social Security Number. If you do not have one, check the “N/A” box. Failure to provide a valid SSN or to check “N/A” will result in form rejection. Also, provide your date of birth using the standard MM/DD/YYYY format.
Line 4: Personal Mailing Address and Phone Number
Provide your complete street address; a P.O. box is allowed only if the post office does not deliver mail to your street address. Include city, state or province, country (do not abbreviate), and ZIP or postal code. Also enter a personal phone number where you can be reached.
Line 5a: Business Mailing Address and Phone Number
If your business address is the same as your personal mailing address, check the box. If different, provide your complete business address, phone numbers (domestic and international), city, state or province, country, and postal code.
Line 5b: Business Identification
Indicate whether you are self-employed or hold a role such as owner, partner, or officer in a tax return preparation business. If “Yes,” fill in the business name, your CAF number (if applicable), Employer Identification Number (EIN), Electronic Filing Identification Number (EFIN), and optionally your business website. If “No,” skip to Line 6.
Line 6: Email Address
Enter a valid email address where you can be reached consistently. The IRS uses this contact for communications.
Line 7: Past Felony Convictions
You must indicate whether you have been convicted of a felony in the last 10 years by checking “Yes” or “No.” If “Yes,” you must provide an explanation detailing the date and nature of the conviction(s). Leaving this line blank causes processing delays or rejection.
Line 8: Address of Your Last U.S. Individual Income Tax Return Filed
Enter the address used on the most recent individual federal tax return you filed. If you have never filed a U.S. federal tax return or are not required to file one, check the appropriate box and see instructions for required documentation if this is your initial application.
Line 9: Filing Status and Tax Year on Last U.S. Individual Income Tax Return Filed
Check your filing status from the options: Single, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, Head of Household, or Qualifying Widow(er) with Dependent Child. Enter the tax year (YYYY) of your last federal return. If more than 4 years ago, additional guidance may apply.
Line 10: Federal Tax Compliance
You must certify whether you are current on your individual and business federal taxes, including corporate and employment tax obligations. If you have never filed a return because you are not required to, check “Yes.” If not current, provide an explanation. Failure to respond will cause application rejection.
Line 11: Data Security Responsibilities
Acknowledge awareness of the legal requirement for paid preparers to create and maintain a written information security plan that protects taxpayer data and systems. Refer to IRS Publication 5708 and 4557 for details.
Line 12: Professional Credentials
Check all applicable professional credentials you currently hold and which are not expired or retired. Include: Attorney (with jurisdiction(s), license numbers, and expiration dates), Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Enrolled Agent (EA), Enrolled Actuary, Enrolled Retirement Plan Agent (ERPA), State Regulated Tax Return Preparer (with jurisdiction(s), license numbers, and expiration dates), and Certifying Acceptance Agent (CAA). Leave blank if none.
Line 13: Fees
The PTIN processing fee is $19.75 for 2025. Include full payment via separate check or money order(s) for each calendar year applying or renewing. Indicate the intended calendar year on each payment. Do not staple or attach payments to the form. Failure to pay or returned payments results in PTIN suspension.
Signature Section
Sign the form “Under penalties of perjury” declaring the form’s accuracy and correctness. Use blue or black ink. Enter the date of signing in MM/DD/YYYY format. Note: Foreign preparers without a U.S. issued SSN cannot prepare federal tax returns for compensation in the U.S.